If you are a person whose life is closely connected with music or you are engaged in sound recording – have you ever been interested in the principle of operation of microphones and their types. Today we will talk about condenser microphones and what they serve for.
You may also like: 9 Best Voiceover Microphones
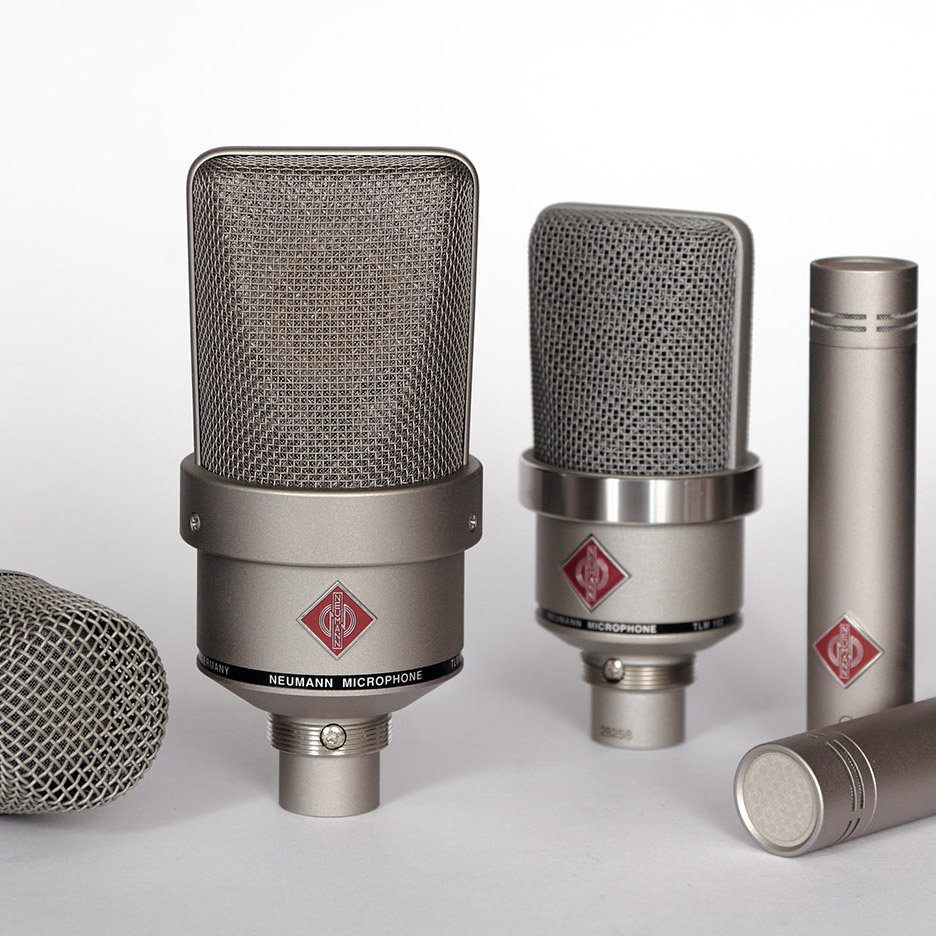
What is a condenser microphone?
Condenser microphone – unlike other, it has a more complex principle of operation. It is based on a capacitor (which actually can be understood by the name). Its capacity depends on the distance between the plates – the larger it is, the smaller the microphone capacity.
The design provides a thin diaphragm, which is located at the microphone plate itself. The capsule is made of conductive materials similar to a thin layer of foil.

When colliding with the microphone diaphragm, the sound wave oscillates relative to the metal plates, changing the distance between them.
That is, the principle of operation of condenser microphones is based on the conversion of sound energy into electrical sound.
Due to the voltage difference between the current and the microphone capsule, a converter is used. It is he who amplifies the intensity of the current and makes the output signal as powerful as possible.
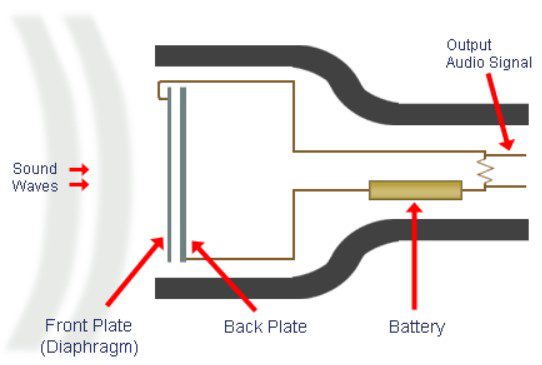
The sound is reproduced thanks to one of the plates – under the influence of sound from the external environment, it causes vibrations already on the capacitor itself, resulting in the same electrical vibrations that transmit sound from the outside.
The plate of a condenser microphone changes its position and direction more easily, it is distorted more precisely under sound waves, which is why a condenser microphone provides more accurate and high-quality sound (compared to other types of microphones
However, despite a number of advantages, this type of microphones has a sufficient number of disadvantages. The condenser microphone has the following disadvantages:
- All models of condenser type microphones have a parameter of maximum sound volume. This implies that you set the device boundaries will not work.
- This type of microphone is unstable to environmental changes –its operation is strongly affected by temperature and humidity changes. If the environmental indicators are too unstable, this can lead to the failure of the device or a serious malfunction.

Despite their disadvantages, condenser microphones continue to be actively used because of their excellent sensitivity. Thanks to them, you can get a softer and more natural sound.
That is why this type of microphone is used if you need the highest sound quality.
It should be remembered that the operation of condenser microphones (for most models) requires phantom power. But fortunately, today most manufacturers make microphones with internal built-in phantom power.
So before you go to the store to purchase phantom power, familiarize yourself with the contents of your device and how it works.
In studios, condenser microphones are recommended for recording most percussion instruments, vocals, podcasts, electric bass instruments, acoustic instruments (guitars, pianos, strings and wind instruments)
You may also like: 11 Best microphones for interviews
Connecting a microphone
For both the microphone and the preamp, it will be better if you connect them to each other before the phantom power is turned on. It is also advisable to disconnect the phantom before disconnecting the cables.
More importantly, it is necessary to ensure that the channel faders or control volume controls are set to zero when the phantom power is turned on or off, since loud bangs and clicks that often occur when the phantom is turned on can damage your speakers or even your ears.
Most professionals will always turn the microphones on and off “hot”, while the phantom power is already on.
However, it is believed that such actions can damage the electronic components inside the microphone and preamp or lead to an increase in noise levels.
Thus, the safest practice is as follows: first set the faders to zero (or turn on MUTE mode, and then turn on the phantom power.
Before we finish with the topic of phantom power, it’s worth mentioning one more thing. Some equipment, especially portable devices, provide a phantom supply voltage below the standard level of 48 V.
You may also like: 11 Best microphones for streaming
As already mentioned, some microphones will operate at lower voltages, by increasing the supply current and possibly narrowing the dynamic range (that is, the maximum sound level they can process without distortion), while others will not work at all.
The specification that comes with the microphone will tell you which phantom power supply voltage range is applicable for this microphone model.

Some microphone manufacturers claim that their products are so reliable that they can hammer nails with it. And this may actually be true, but we would not recommend using microphones as a hammer.
Especially in the case of a condenser microphone, since its capsule is a very complex and delicate device.
Although modern models are more reliable than those manufactured in the past, but keep in mind that condenser microphones do not tolerate drops and bumps very well.
When installing the microphone on a rack, it is best to loosen the attachment latch on the rack or boom lever so that it can rotate freely.
Then, holding the microphone firmly, turn the stand or boom lever so as to screw it into the thread of the microphone stand adapter.
What do I need to know before using a microphone?
In no case should sprays be used to clean the contacts, they can drift onto the microphone diaphragm, bringing irreparable damage to it. Smoke particles, dust and other air pollution can also settle on the diaphragm and cause problems.
Despite the fact that, theoretically, the diaphragms can be cleaned, this is a very complex and, therefore, expensive process. This is not something you should ever do at home!
Undoubtedly, the most common problem with condenser microphones arises from fluctuations in air humidity, although, fortunately, this is usually only a temporary problem.

Warm moist air will condense on the cold metal, and the water is sufficiently conductive to facilitate the discharge of charges from the membrane.
This often happens if you bring a cold microphone into a warm studio or the vocalist is working very close to the microphone.
You may also like: 9 Best 3.5mm Microphones
Moisture from the singer’s breath can condense on the diaphragm and cause unpleasant crackling and hissing noises. A properly positioned pop filter in most cases allows you to avoid this.
When calculating the temperature, you should wait for the condenser microphone to warm up to room temperature before using.